Angular code coverage using CircleCI and Coveralls
Hello Angular
Angular out of the box is packed with great tools and templates to scaffold a new project in a few minutes.
Install Angular CLI if you do not have it yet using instructions from CLI Command Reference.
Create a new project:
ng new angular-hello-world
cd angular-hello-world
ng test --watch=false --code-coverage
Last command runs unit tests included into the scaffolded project and calculates code coverage.
You should see something like output below if everything was done right:
Chrome 73.0.3683 (Mac OS X 10.14.3): Executed 3 of 3 SUCCESS (0.25 secs / 0.223 secs)
TOTAL: 3 SUCCESS
=============================== Coverage summary ===============================
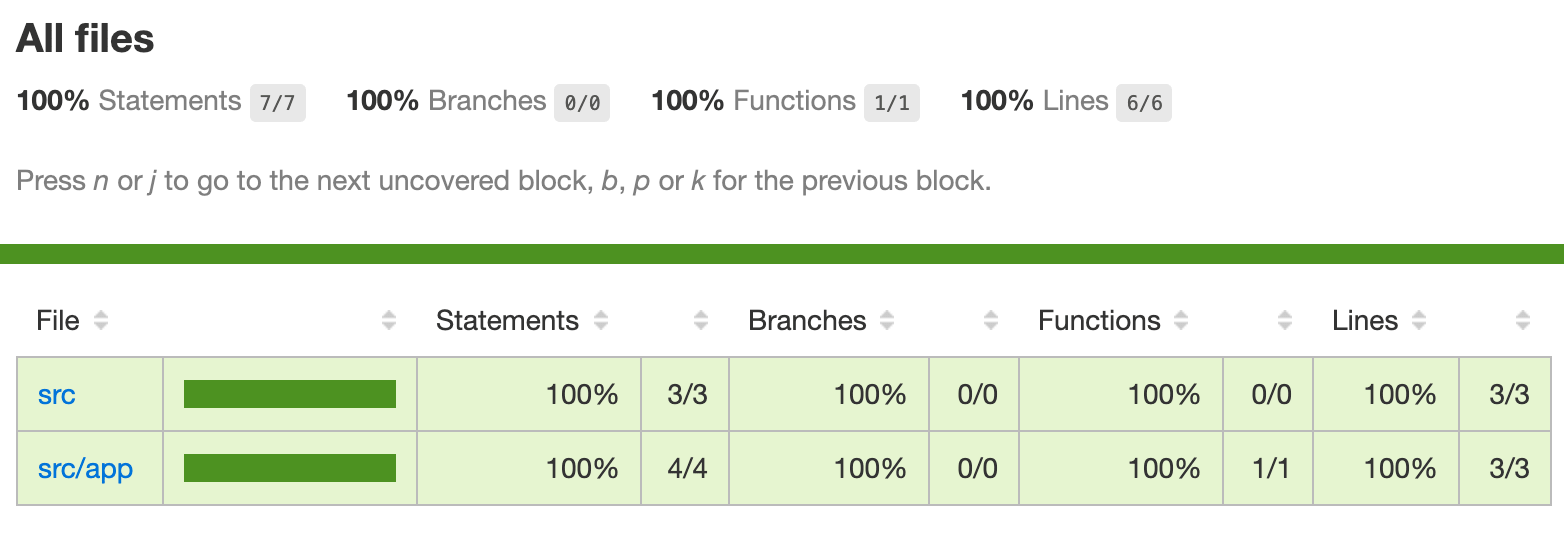
Statements : 100% ( 7/7 )
Branches : 100% ( 0/0 )
Functions : 100% ( 1/1 )
Lines : 100% ( 6/6 )
================================================================================
TOTAL: 3 SUCCESS
TOTAL: 3 SUCCESS
Code coverage files stored in /coverage folder. Open /coverage/angular-hello-world/index.html file in browser to see results:
Get Coveralls access token
Hint: Project should be pushed to GitHub to use Coveralls.
Sign in into Coveralls using your GitHub credentials.
Go to Add Repos page.
Hint: click
SYNC REPOSbutton at the top right corner of the screen if you do not see your repo.
Find your project in the list of available projects and enable it:

Go to details and record secret access token, you will need it later.
Install Coveralls package
We need to install npm package that enables pushing coverage results to Coveralls:
npm install coveralls --save-dev
Post to Coverage from local machine
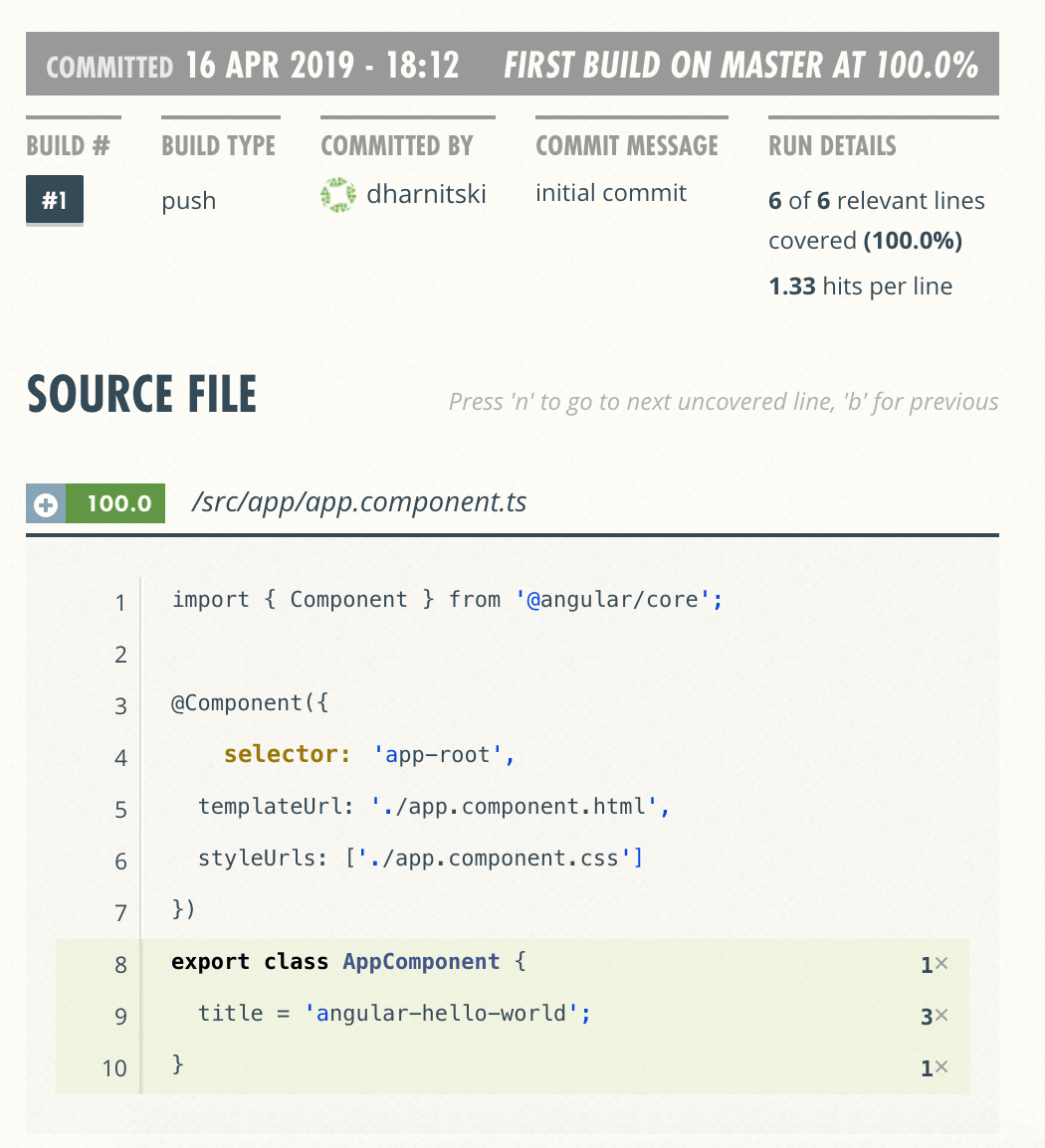
Let’s test if we can post generated test coverage to Coveralls.
Hint: Coveralls uses
lcov.infofile to read code coverage lines. This file is generated out of the box if you used Angualar project scaffolding.
Create .coveralls.yml file in project root and paste secret token into created file:
repo_token: <coveralls-secret-token>
Important: Do NOT commit this file into GIT. Delete it or add into
.gitignoreafter you are done with testing.
Run command line to push code coverage:
cat ./coverage/angular-hello-world/lcov.info | ./node_modules/coveralls/bin/coveralls.js
You can see code coverage being published now:
Add .circleci/config.yml
Angular documentation includes sample for testing project using Circle CI.
Check it to see if anything is changed after this post is published.
Our script adds a few extra lines to integrate with Coveralls:
version: 2
jobs:
build:
working_directory: ~/my-project
docker:
- image: circleci/node:10-browsers
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
key: my-project-{{ .Branch }}-{{ checksum "package-lock.json" }}
- run: npm install
- save_cache:
key: my-project-{{ .Branch }}-{{ checksum "package-lock.json" }}
paths:
- "node_modules"
- run:
name: Lint
command: npm run ng lint
- run:
name: Unit Test
command: npm run ng test -- --watch=false --code-coverage
- run:
name: Coveralls
command: cat ./coverage/angular-hello-world/lcov.info | ./node_modules/coveralls/bin/coveralls.js
Configure CircleCI
Login into CircleCI using GitHub credentials and Set Up yor project.
Hint: You can skip configuration steps as it is only generates
.circleci/config.ymlfile that we already have. You can safely clickStart buildingbutton as soon as you see it.
Go to project setting in CircleCI and add environment variable COVERALLS_REPO_TOKEN with value storing secret Coveralls access token.
Now everything is configured. Every push into every branch triggers build using CircleCI and publishes code coverage.
It is also a right time to enforce coverage rules or setup pull request alerts.
Badges
Do not forget to add Coveralls and CircleCI badges to README.md file.
Happy Covering!